Abstract
Introduction: Despite the clinical success of CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed / refractory (r/r) LBCL (large B-cell lymphoma), the majority of patients do not respond or relapse early after treatment. Biomarker analysis within pivotal trials showed the prognostic value of CAR T-cell expansion over time during the early post-transfusion period. We set up a longitudinal immunomonitoring to investigate whether distinct CAR T-cell levels can predict treatment response.
Methods: 63 patients with r/r LBCL were treated in third line with the commercially available CD19-directed CAR T-cell products Axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi-cel) or Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-cel) between January 2019 and November 2021 at the University Hospitals of Erlangen and the LMU Munich. Aliquots of CAR T-cell products and EDTA-anticoagulated peripheral blood (15cc) were collected at day 4, 7, 14, 28, 60 and 90 post CAR T-cell transfusion. Clinical metadata were assembled prior and post transfusion. CAR T-cells were analyzed with flow cytometry utilizing a two step-staining with a biotinylated CD19 protein. CAR T-cells were detected with a sensitivity of 1:2000 and reported as cells/µl based on differential blood counts. Responders (R, complete or partial remission) were compared to non-responders (NR, stable or progressive disease) according to (PET-) CT scans three months after transfusion.
Results: Surprisingly, the CAR T-cell products contained more untransduced T-cells than anti-CD19 expressing CAR T-cells with a median cell number of 5.75x108 Non-CAR T-cells and 1.76x108 CAR T-cells (p<0.0001). Even though a large inter-patient variability was observed, CAR T-cell peak expansion occurred between day 7 to 14 in the majority of patients. Interestingly, differences in the number of CAR T transduced T-cells were observed in Tisa-cel versus Axi-cel: Tisa-cel products contained higher numbers of Non-CAR T-cells compared to Axi-cel products (p<0.0001) followed by greater expansion of Non-CAR T-cells over time after Tisa-cel transfusion compared to Axi-cel transfusion (p=0.0155).
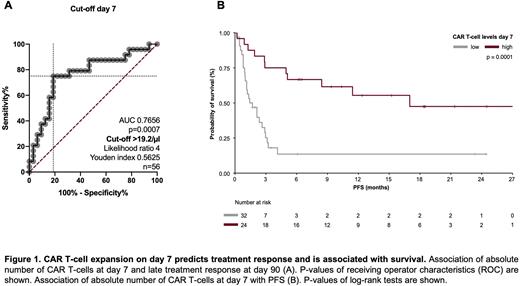
However, the absolute number of CAR T transduced T-cells within the product did not impact response rate. More importantly, higher CAR T-cell expansion over time (AUC p=0.0007) and peak expansion (p=0.0009) were associated with treatment response. Moreover, higher CAR T-cell peak expansion in relation to tumor burden at baseline was associated with treatment response (p=0.0011). Comparing the absolute CAR T-cell numbers at the different time points, we identified the CAR T-cell levels at day 7 to be strongly associated with treatment response (p=0.0005). Next, through ROC analysis, we were able to identify 20/µl CAR T-cells on day 7 as a cut-off value, that was associated with treatment response (AUC=0.7656 and p=0.0007) and improved survival (PFS p=0.0001 and OS p=0.0002). Next, we hypothesized, that higher CAR T-cell numbers on day 7 reflect the superior capacity of CAR T-cells to proliferate and expand. This was indeed supported by our findings, that CAR T-cell numbers on day 7 correlated with the absolute number of CAR T-cells in the CAR product of R (r=0.4928, p=0.0144) but not of NR (r=-0.152). Finally, we found patient- (ECOG) and disease-associated (tumor volume, LDH) as well as baseline inflammatory markers (CRP and Ferritin) to be negatively correlated with CAR T-cell kinetics.
Conclusion: Longitudinal quantification of CAR-T cells by multiparameter flow cytometry is feasible. Responding patients with r/r LBCL showed greater CAR T-cell expansion over the first 90 days post transfusion. Notably, a cut-off value of 20/µl CAR T-cells at day 7 was associated with both improved radiographic response and survival. Currently the cut-off value is being validated in an external control of 100 patients. Our data suggest that quantification of CAR T-cell levels might serve as a biomarker to predict treatment failure and open up the possibility to modify treatment concepts in these patients at an early time point.
Disclosures
Blumenberg:BMS/Celgene: Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Consultancy, Other: congress and travel support, Research Funding; Janssen: Other: congress and travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding. Rejeski:Kite/Gilead: Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria. Schmidt:BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; Bayer Healthcare: Research Funding; Janssen: Other: Travel Support; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support; Kite Gilead: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: Travel Support. Mueller:Novartis: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria; MedImmune: Research Funding. Mougiakakos:Jazz Pharma: Honoraria; Gilead: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Bücklein:Miltenyi: Research Funding; Janssen: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: congress and travel support, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: congress and travel support, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Speakers Bureau. Mackensen:Miltenyi Biomedicine: Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Kite/Gilead: Honoraria. Subklewe:Seagen: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Miltenyi Biotech: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Takeda: Other: Travel support; Morphosys: Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.